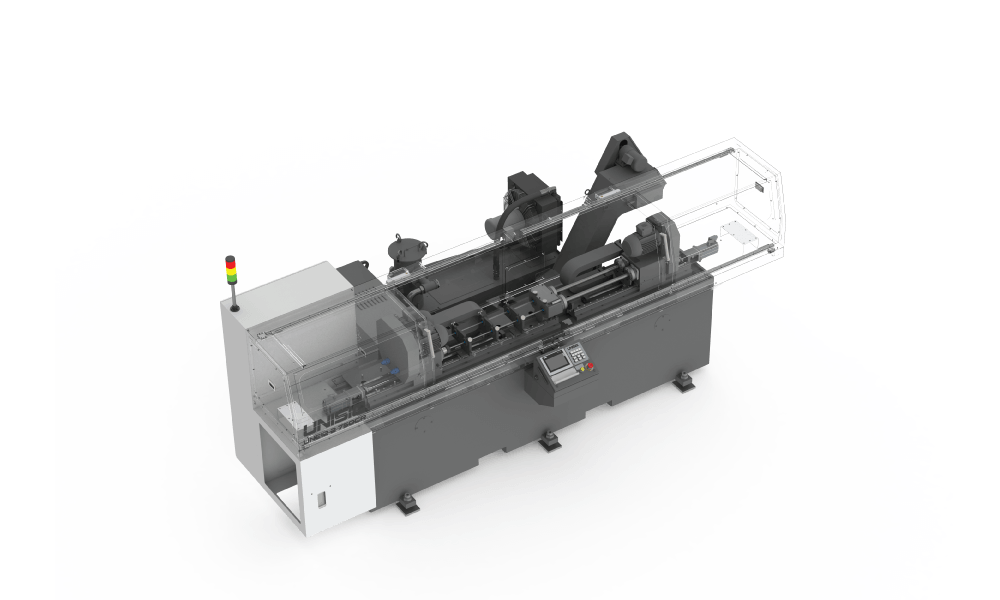
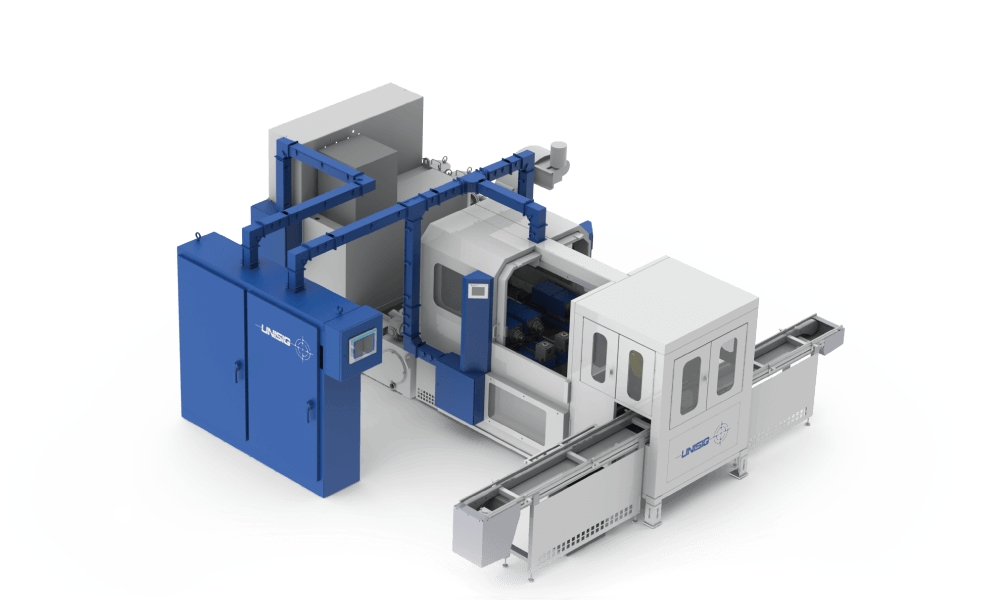
Gundrill Machine Overview
What Is a Gundrilling Machine?
Gundrilling machines a type of deep hole drilling machine, engineered and built to maximize the performance of gundrill tooling, in order to drill very deep, precision holes in virtually any material. Specialized machinery integrates capable technology required for tool support, coolant pressure, and machine power to handle deep hole gundrilling applications accurately and efficiently.
Machines are built on proven technology and typically configured based on workpiece size and shape, required production rates, and precision specifications.
How Drilling Works on a Gundrilling Machine
Coolant is delivered through the center of the gundrill tool, while a motor turns either the tool or the workpiece or both. A feed system provides thrust to the tool to begin gundrilling. The tool is guided accurately into the workpiece by a bushing.
While drilling, chips are flushed out along the gundrill flute by the force of high-pressure coolant. No peck drilling or interrupted feed is necessary to clear the chips.
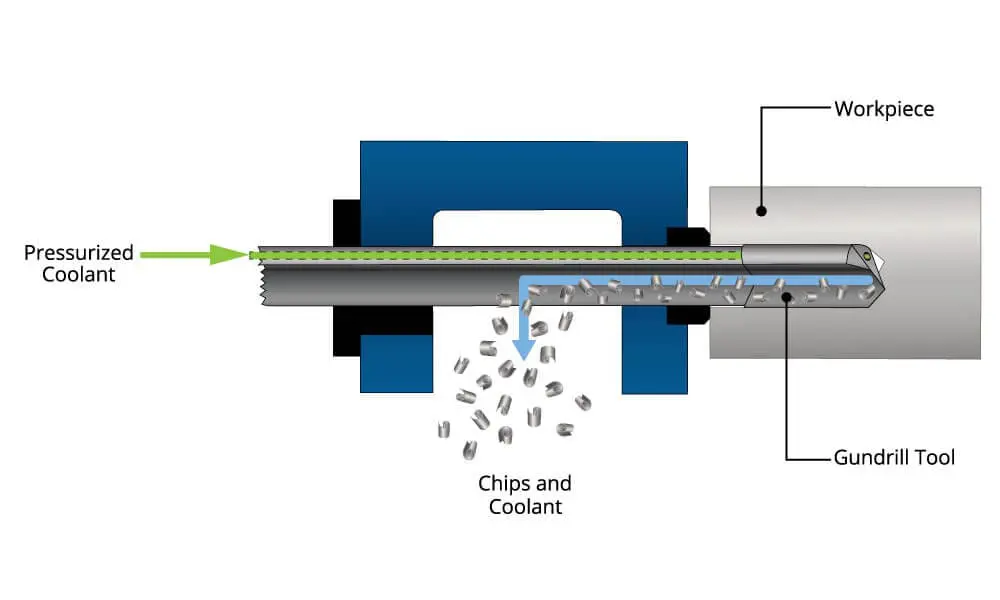
Full Schematic of a Typical Gundrilling Machine
Key Components for Gundrilling Machines
Several components are present on typical gundrilling machines, regardless of configuration.
Drill Guide Bushing
A precision drill guide bushing contacts the workpiece to guide the gundrill tool as it prepares to drill. This bushing allows the tool to start in the proper location, and with the correct hole diameter, both essential for accurate deep hole drilling. The drill guide bushing also works to seal against the workpiece to contain the coolant during the drilling process.
Chip Box
The chip box is a precision-machined component that maintains critical alignment between the drill guide bushing and spindle centerline. As the chips are flushed out of the opening by the cutting fluid flow, a feature in the machine structure redirects the chips and fluid from the gundrilling operation, while containing it for a clean, mess-free gundrilling machine and surrounding area.
Whip Guides
Whip guides support long tools outside of the workpiece, as high speed and imbalanced nature of gundrill tools create whip. Whip guides are devices equipped with rotating bearings and inserts that contact the tool, and stabilize the shank during the drilling process. Longer travel machines may have six or more traveling whip carriages that collapse into each other as the tool moves, while shorter drilling machines may only have a single stationary guide.
Drilling Spindle
The gundrilling machine spindle transmits power and torque from the motor with high speed, high precision, and low vibration, for productive gundrilling. Spindles also run at very high duty cycles, and thus are engineered to last under these conditions. Belt driven spindles are common, but higher speed applications may require an integral motor.
Coolant System
The reliability and performance of the gundrilling process depends heavily on the machine coolant system. A logically designed reservoir system starts by holding coolant, and a high-volume pump groups works to delivery the cutting fluid to the gundrill tool. Once the coolant progresses through the metal cutting operation, it is enters the filtration system. Low-micron coolant filtration, and filter condition feedback prevent the accumulation of chips and small particles, leading to less down time, longer tool life, and improved surface finishes.
Coolant Temperature Control
The drilling headstock, the drilling process and coolant pumping system generate heat, which can have a negative impact on drilling factors such as tool life and accuracy, as well as the operating conditions around the machine. To manage the heat, either a heat exchanger or chiller is required to maintain cutting fluid at the proper temperature.